Breast cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide, affecting millions of individuals each year. Understanding breast cancer is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This article delves into the causes of breast cancer, highlighting genetic and environmental factors, as well as the key symptoms to watch for. By exploring current treatment options, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate this challenging condition with confidence.
Breast cancer is a significant health concern that impacts both women and men across the globe. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essential aspects of breast cancer, including its causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment strategies. Whether you’re seeking information for personal knowledge or to support a loved one, understanding breast cancer is the first step toward effective management and prevention. Join us as we break down the complexities of this disease and offer valuable insights.
When it comes to breast cancer, knowledge is power. This article provides a thorough overview of breast cancer, from its underlying causes and risk factors to the symptoms that may indicate its presence. We will also discuss the most recent advancements in treatment, helping you stay informed about the best approaches to tackle this condition. Understanding breast cancer is vital for taking proactive steps in your health journey or supporting others through their battle.
Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent and researched cancers, with ongoing advancements in both understanding and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of breast cancer, including what causes it, the symptoms to be aware of, and the latest treatment options available. By enhancing your knowledge about breast cancer, you can better navigate the complexities of this condition and make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Overview of Breast Cancer
An overview of breast cancer is essential for understanding the breadth of this prevalent disease and its impact on individuals and communities. Breast cancer, a condition where malignant cells form in the tissues of the breast, affects millions worldwide. By gaining a thorough overview of breast cancer, you can grasp its complexity, including how it develops, the various types, and the factors contributing to its onset. This foundational knowledge is crucial for recognizing early signs, seeking timely medical intervention, and improving overall awareness and education about the disease.
Understanding the overview of breast cancer provides critical insights into the disease’s progression and treatment options. Breast cancer encompasses various stages and types, each with unique characteristics and implications for treatment. A comprehensive overview of breast cancer helps demystify the condition, making it easier to understand the importance of early detection, diagnostic procedures, and therapeutic strategies. This clarity can empower patients and their families to make informed decisions and actively participate in the management of their health.
The importance of an overview of breast cancer cannot be overstated, as it lays the groundwork for effective prevention and intervention strategies. Breast cancer affects not only the individual diagnosed but also their families and communities. By exploring the basic concepts and details of breast cancer, individuals can better appreciate the significance of regular screenings, risk assessments, and advances in research. An informed perspective on breast cancer enables proactive measures and fosters a supportive environment for those affected by the disease.
Importance of Understanding Breast Cancer
Understanding breast cancer is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of this prevalent disease. Breast cancer, which involves the abnormal growth of cells in the breast tissue, can significantly impact one’s health and quality of life. By grasping the importance of understanding breast cancer, individuals can better recognize early symptoms, comprehend various treatment options, and engage in proactive health measures. This awareness not only aids in early detection but also improves outcomes by enabling timely and informed medical decisions.
The importance of understanding breast cancer extends beyond personal health to broader public awareness and support. Breast cancer affects millions of people worldwide, making it essential to educate ourselves about its causes, symptoms, and treatments. This knowledge helps reduce stigma, supports research efforts, and promotes preventive strategies within communities. By fostering a deeper understanding of breast cancer, we can contribute to more effective public health initiatives and support systems for those affected by the disease.
A comprehensive understanding of breast cancer is vital for effective disease management and support. Knowing the details about breast cancer, including its risk factors and treatment options, empowers patients and their families to make informed choices about their health. It also enhances communication with healthcare providers, facilitating better care and management. Emphasizing the importance of understanding breast cancer ensures that individuals are equipped with the knowledge needed to confront the disease with confidence and resilience.
What is Breast Cancer?
Definition and Types
Breast cancer is defined as a malignancy that originates in the cells of the breast, leading to abnormal growths or tumors. This disease can occur in different parts of the breast tissue, including the ducts and lobules. Understanding the definition of breast cancer is crucial for recognizing its early signs and seeking timely treatment. By defining breast cancer and its various types, individuals can better grasp the nature of the disease and the importance of early detection and intervention.
Breast cancer encompasses several types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. The most common types include invasive ductal carcinoma, which starts in the milk ducts, and invasive lobular carcinoma, which begins in the lobules. There are also non-invasive forms, such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), where cancer cells are confined to the ducts. Understanding the different types of breast cancer helps in tailoring treatment plans and managing the disease effectively.
The definition and types of breast cancer play a critical role in determining the appropriate course of action for patients. Each type of breast cancer, from invasive to non-invasive, presents unique challenges and treatment options. By familiarizing oneself with the various forms of breast cancer, individuals and healthcare professionals can work together to develop a personalized treatment strategy. This knowledge not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also in optimizing treatment outcomes and improving overall patient care.
How Breast Cancer Develops
Breast cancer develops when cells in the breast tissue begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. This process starts at the cellular level, where mutations in the DNA cause normal breast cells to become cancerous. Understanding how breast cancer develops is crucial for recognizing the early warning signs and seeking prompt medical attention. By identifying the factors that contribute to the growth of breast cancer cells, individuals can take proactive steps towards early detection and effective treatment.
The development of breast cancer involves a series of stages, beginning with the transformation of normal cells into malignant ones. Initially, abnormal cells may form a lump or mass within the breast, which can then invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Factors such as genetic predispositions, hormonal imbalances, and environmental influences play significant roles in how breast cancer develops. Gaining insight into these processes helps in understanding the complexities of the disease and emphasizes the importance of regular screenings.
How breast cancer develops is influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Mutations in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of developing breast cancer. Additionally, long-term exposure to estrogen and other hormones can contribute to the growth of cancerous cells. By exploring the mechanisms behind the development of breast cancer, individuals can better understand their own risk factors and the preventive measures that can be taken to reduce their chances of developing the disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a crucial role in the development of breast cancer, with certain inherited mutations significantly increasing the risk. Breast cancer can run in families, often due to mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2. These genetic changes can be passed down from one generation to the next, making it essential to understand how genetics influence the likelihood of developing breast cancer.
Individuals with a family history of breast cancer are at a higher risk due to genetic predispositions. Inheriting mutations in specific genes can lead to a higher chance of developing breast cancer at a younger age. Genetic testing and counseling are important for those with a family history, as they can help assess risk and guide preventive measures.
Understanding genetic factors in breast cancer helps in identifying individuals at increased risk and allows for more personalized prevention strategies. Advances in genetic research have provided valuable insights into how mutations contribute to breast cancer, leading to better screening protocols and targeted treatments for those with inherited risk factors.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental and lifestyle factors can significantly influence the risk of developing breast cancer. Exposure to certain environmental pollutants and toxins has been linked to an increased risk of the disease. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and smoking habits play a role in breast cancer risk, highlighting the importance of healthy living.
Diet and physical activity are key components in managing breast cancer risk. Studies have shown that a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, along with regular exercise, can help lower the risk of developing breast cancer. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits may contribute to higher risk levels.
nvironmental exposures, such as radiation and chemicals, can also impact breast cancer risk. Reducing exposure to known carcinogens and making healthier lifestyle choices are proactive steps individuals can take to mitigate their risk of breast cancer. Awareness and preventive measures related to environmental and lifestyle factors are essential for long-term health.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal influences are a significant factor in the development of breast cancer. Estrogen and progesterone, two key hormones, can fuel the growth of certain types of breast cancer. Understanding how these hormones affect breast tissue is crucial for managing hormone-related cancer risks and tailoring treatment strategies.
Long-term exposure to estrogen, such as through hormone replacement therapy or early onset of menstruation, has been linked to an increased risk of breast cancer. Monitoring hormonal levels and understanding their impact on breast cancer risk can help in making informed decisions about hormone-related treatments and preventive measures.
Hormonal influences on breast cancer also extend to reproductive history, such as the age of first childbirth and the number of pregnancies. These factors can affect hormone levels and influence breast cancer risk. By understanding how reproductive and hormonal factors interplay with breast cancer development, individuals can better assess their risk and make proactive health choices.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender are important considerations when discussing breast cancer risk. While breast cancer is more common in women, men can also develop the disease, though it is rarer. The risk of breast cancer increases with age, making regular screenings and awareness particularly important for older adults.
For women, age plays a critical role in breast cancer risk, with the likelihood increasing as they grow older. Women over the age of 55 are generally at higher risk, which underscores the importance of regular mammograms and preventive care as part of routine health maintenance for older women.
Gender differences in breast cancer incidence highlight the need for tailored awareness and prevention strategies. While breast cancer in men is less common, it is important for both men and women to understand their unique risk factors related to age and gender. Early detection and awareness can significantly improve outcomes for all individuals affected by breast cancer.
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
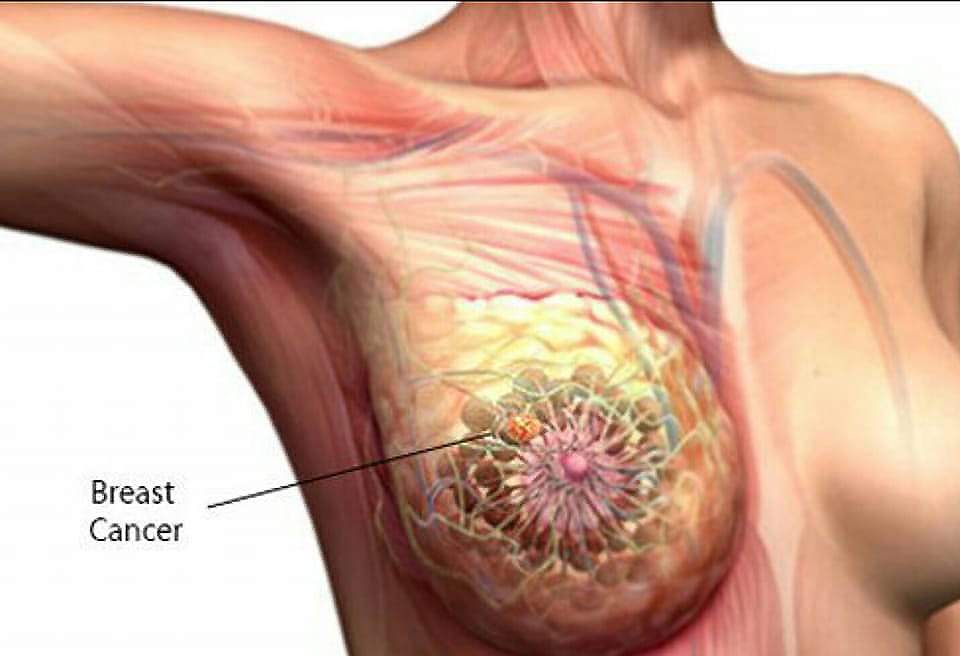
Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the early warning signs of breast cancer is crucial for effective early detection and treatment. Early symptoms may include changes in the breast or nipple, such as a lump or swelling, even if it is painless. Being aware of these initial signs can lead to prompt medical evaluation and increase the chances of successful treatment.
Another early warning sign of breast cancer is unusual changes in breast texture or color. If you notice areas of redness, warmth, or a change in the skin’s appearance, it may be indicative of breast cancer. Early detection through monitoring these signs can help ensure timely intervention and improve overall outcomes.
Nipple discharge, particularly if it is bloody or occurs without any apparent reason, can also be an early warning sign of breast cancer. While not all nipple discharges are cancerous, it’s important to report any unusual symptoms to a healthcare provider for further investigation and appropriate action.
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of breast cancer often include the presence of a noticeable lump or mass in the breast or underarm area. These lumps can vary in size and may feel different from the surrounding tissue. Identifying these common symptoms early can prompt individuals to seek medical evaluation and potentially detect breast cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage.
Breast cancer can also manifest through changes in breast size or shape, such as a noticeable dimpling or puckering of the skin. These symptoms, along with persistent pain or discomfort in the breast, can be indicative of cancer. Understanding these common symptoms is key to early detection and effective management of the disease.
In addition to lumps and changes in breast appearance, swelling or tenderness in the breast area can be a common symptom of breast cancer. Even if the swelling is localized or intermittent, it’s important to have these symptoms evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out or confirm the presence of breast cancer.
How Symptoms Differ by Stage
The symptoms of breast cancer can vary significantly depending on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, breast cancer may present with subtle signs, such as a small lump or localized swelling. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may become more pronounced, including larger tumors, significant changes in breast shape, and potential spread to nearby lymph nodes.
In advanced stages of breast cancer, symptoms can include more severe manifestations, such as significant changes in breast texture, persistent pain, and the development of skin ulcers. Additionally, metastatic breast cancer can lead to symptoms beyond the breast, such as bone pain or breathing difficulties if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Understanding how symptoms of breast cancer differ by stage is essential for effective monitoring and treatment. Early-stage breast cancer often involves fewer and less severe symptoms, while later stages may present with a wider range of complications and more aggressive symptoms. Recognizing these differences helps in assessing the progression of the disease and determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment Options
Surgery: Types and Procedures
Surgery is a common treatment option for breast cancer and involves several types of procedures depending on the stage and location of the cancer. The two main types are lumpectomy, where only the tumor and a small margin of surrounding tissue are removed, and mastectomy, which involves the removal of one or both breasts. Understanding these surgical options is essential for making informed decisions about breast cancer treatment.
In addition to lumpectomy and mastectomy, some patients may require axillary lymph node dissection, which involves the removal of lymph nodes under the arm to check for cancer spread. This procedure helps in assessing the extent of breast cancer and planning further treatment. Knowing the various surgical procedures for breast cancer can help patients and their families prepare for the recovery process.
Reconstructive surgery is often considered after a mastectomy to restore the appearance of the breast. Options include implant-based reconstruction or autologous tissue reconstruction, where tissue from another part of the body is used. Understanding the different types of reconstructive surgery available for breast cancer patients can aid in making choices that align with personal preferences and treatment goals.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a critical component of breast cancer treatment that uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is often used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancerous cells in the breast, chest wall, or underarm area. Radiation therapy helps reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and is an essential part of the post-surgical treatment plan for many breast cancer patients.
The most common form of radiation therapy for breast cancer is external beam radiation, where a machine directs radiation precisely at the affected area. This type of radiation therapy typically involves daily sessions over several weeks. Understanding how radiation therapy works and its role in breast cancer treatment can help patients better prepare for and manage their treatment experience.
Radiation therapy for breast cancer may also include techniques like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) or proton therapy, which aim to minimize damage to healthy tissues while targeting the cancerous cells. Exploring these advanced radiation techniques can provide additional options for patients seeking effective and personalized treatment approaches.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment used to combat breast cancer by targeting and killing fast-growing cancer cells throughout the body. It is often administered before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy) to shrink tumors or after surgery (adjuvant therapy) to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Understanding how chemotherapy works and its potential benefits is crucial for patients navigating their breast cancer treatment options.
Chemotherapy for breast cancer typically involves a combination of drugs administered intravenously or orally in cycles. The treatment plan is tailored based on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Being aware of the various chemotherapy drugs and regimens can help patients prepare for potential side effects and manage their treatment more effectively.
Side effects of chemotherapy for breast cancer can include nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and changes in appetite. While these effects can be challenging, there are strategies and medications available to help manage them. Understanding the potential side effects of chemotherapy and how to address them is an important part of the breast cancer treatment journey.
Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal therapy, also known as endocrine therapy, is used to treat breast cancer that is hormone receptor-positive. This treatment works by blocking the effects of estrogen or reducing its levels in the body, which can help slow or stop the growth of hormone-sensitive cancer cells. Hormonal therapy is a key component in managing certain types of breast cancer and preventing recurrence.
Common forms of hormonal therapy for breast cancer include selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors such as letrozole. These medications are typically prescribed for several years after initial treatment to reduce the risk of cancer returning. Understanding the role of hormonal therapy in breast cancer treatment helps patients adhere to their treatment plans and optimize outcomes.
Hormonal therapy may also involve ovarian suppression or ablation for premenopausal women, aiming to reduce estrogen production. This approach can be combined with other hormonal therapies to enhance effectiveness. Knowing the different hormonal therapy options and their mechanisms provides valuable insight into how they contribute to the management of breast cancer.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy for breast cancer focuses on specific molecular targets associated with cancer cells, such as HER2 proteins. Drugs like trastuzumab (Herceptin) are designed to target and inhibit these proteins, which can help slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells. Targeted therapy is often used in combination with other treatments to enhance its effectiveness against breast cancer.
Immunotherapy is an emerging treatment option that aims to boost the body’s immune system to better recognize and attack cancer cells. While still primarily used in clinical trials for breast cancer, immunotherapy shows promise for certain subtypes, such as triple-negative breast cancer. Understanding the potential of immunotherapy and its role in breast cancer treatment can offer hope for new and effective treatment approaches.
Both targeted therapy and immunotherapy represent significant advancements in breast cancer treatment, offering personalized approaches based on the genetic and molecular characteristics of the cancer. These therapies provide additional options for patients, particularly those with advanced or difficult-to-treat breast cancer subtypes. Exploring these innovative treatments can help patients make informed decisions about their care and potential benefits.




